4 Approaches to Reducing Data Center Power Consumption for More Sustainable Development
As companies face increasing pressure to meet sustainability goals and comply with regulatory demands, reducing data center energy consumption has become a top priority. AI technologies, from machine learning to autonomous driving, are driving up the power needs of servers. For instance, AI chips now consume up to 700 watts, with future chips expected to use over 1,000 watts. As data centers consume a growing share of total electricity in the coming years, companies must focus on optimizing their IT infrastructure to reduce energy use and enhance sustainability.
The 4 Key Approaches
To minimize data center power consumption, companies should focus on four main areas: hardware component optimization, software strategies, system-level improvements, and application optimization. Each approach aims to enhance energy efficiency and reduce overall energy use. Let’s explore these optimization strategies in detail.
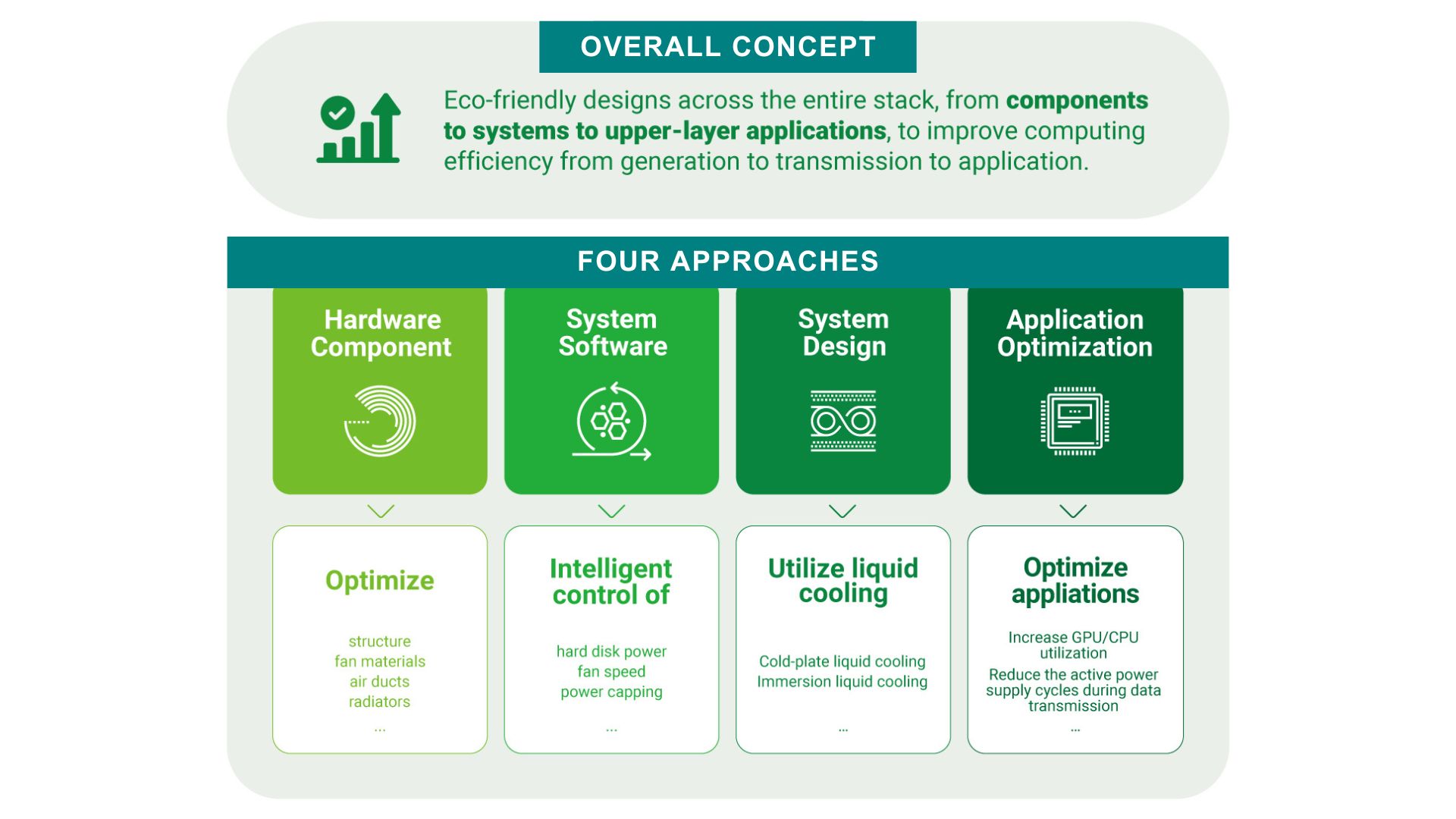
1. Hardware Component Design
Improving hardware design is essential for enhancing energy efficiency. Optimizing the design of hardware components like fans, air ducts, and radiators can significantly boost cooling performance. For instance, refining fan designs, such as better front and rear intakes, can enhance airflow by up to 15% while air duct designs, such as horizontal ducts and honeycomb waveguides, can reduce internal turbulence and improve heat dissipation by over 30%. As IT infrastructure providers continue experimenting with various designs to improve their products and solutions, data center managers should explore and understand the range of cooling solutions available to them to enhance heat dissipation for high-performance processors.
Data centers are handling increasingly powerful processors so improving fan designs, streamlining air ducts, and enhancing cooling techniques will be crucial for maintaining optimal performance while reaching more efficient operations, lower energy costs, and a reduced environmental impact.
2. System Software
At the software level, implementing energy-saving strategies like individual hard disk power control, intelligent speed adjustment, and power limits can cut server power consumption by over 15%.
IT specialists can synchronize hard disk power management with thermal strategies, turning disks on and off as needed, limiting throughput to certain disks, and putting others into sleep mode. Optimizing the heat dissipation strategy also helps by reducing fan speeds and cooling equipment power use. This approach can cut power consumption per terabyte by 315%, save 40% of data center space, and lower operating costs by more than 30%.
Integrated sensors monitor real-time temperatures across the server, enabling precise thermal management. Using decentralized intelligent control, fan speeds, and air distribution are adjusted for efficient cooling and energy savings.
3. System Design
To improve computing efficiency, reduce idle times, and lower energy consumption, IT experts can customize their systems for specific operational needs and use mixed air-liquid or full liquid cooling designs, particularly for high-density and AI servers. This approach can help lower Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) to under 1.2.
Cold plate liquid cooling has proven to be an effective solution for high-power components like processors and memory, which account for over 80% of a data center’s energy use. A cold plate system can cool a 1000-watt chip and handle up to 100 kilowatts of heat in a single cabinet. This cooling method is compatible with various connectors so it reduces server power consumption while minimizing deployment barriers and costs.
Fully liquid infrastructure options are also extremely worth considering. Liquid-cooled racks offer superior energy efficiency, with 50% better heat dissipation and 40% lower power consumption compared to traditional air cooling. Additionally, liquid-cooled servers can handle inlet temperatures of 45°C (113°F), enabling Free-Cooling technology and further reducing energy use in high-temperature environments.
4. Application Optimization
Finally, optimizing the usage of end applications plays a key role in reducing power for better sustainability. IT specialists can optimize server workloads to boost GPU and CPU utilization for consolidation on fewer servers. Pooling together existing computing power and fine-tuning resource allocation strategies can significantly increase GPU usage and potentially improve cluster utilization by over 70%.
Another effective strategy is asynchronous polling, which minimizes active cycles on battery-powered devices during data transfers and communication time to lower overall power consumption.
Improvement is Key to a Better Future
Enhancing data center architecture and management is critical to reducing power consumption and promoting sustainable development. By prioritizing IT infrastructure that balances operational efficiency with compliance with CO2 emissions regulations, businesses can effectively lower costs while fulfilling their sustainability commitments.
